Administration
CRADLE provides administrators with robust tools to manage users, entities, and system-wide settings. This guide explains the key administrative functions and how to use them effectively.
Management Panel
The management panel serves as the central hub for all administrative tasks and is accessible via the Management link in the sidebar. It comprises three main sections:
Entities Management (Accessible to both admins and entry managers)
- Create new entities.
- Edit existing entities.
- Delete entities.
- View entity activity logs (admins only).
- Manage entity metadata and descriptions.
Entry Types Management (Accessible to both admins and entry managers)
- Create new entry classes.
- Edit existing entry classes.
- Define validation rules for artifacts.
- Manage entry type hierarchies.
User Management (Admins only)
- View all system users.
- Manage user permissions.
- View user activity logs.
- Delete user accounts.
- Edit user details using the pencil icon.
- Manage user permissions by clicking on the user.
Details on Entry Classes
Entry classes form the core of how CRADLE organizes data by categorizing pieces of evidence. Each entry class includes the following fields:
Type: Indicates whether the entry is an
entityor anartifact.- Entity: A high-level object of investigation that determines access levels for associated notes.
- Artifact: A piece of evidence that is accessible to all users; any artifact type can be referenced.
Subtype (Name): Defines a unique category for the entry. Examples include
email,username,ip,domain,source, etc.Format: Specifies the valid input for the entry, which can be defined as:
- Regex: A regular expression used to validate the artifact.
- Enumerator: A list of acceptable values, separated by newlines in the admin panel.
Color: Determines the color used for the entry in the knowledge graph.
CaRalyst Type: Associates the entry with a corresponding value in the Catalyst/Blindspot project. It follows the format
type/subtype|model_class|level, where:type/subtyperefers to the threat intelligence object type and its category (e.g.,observables/IP_ADDRESSsends a request to/api/observableswithtype=IP_ADDRESS).model_classis the singular model class of the entry used for linking in Catalyst posts.levelindicates the entry’s linkage level in Catalyst posts (e.g.,OPERATIONAL).
Details on Logs
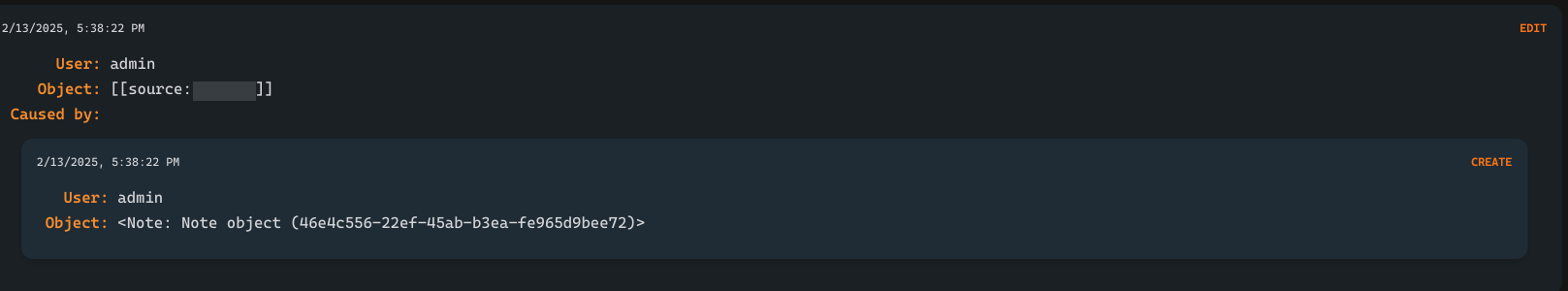
CRADLE maintains extensive logs for all system activity. Each log entry captures three core elements:
- User: The individual who performed the action.
- Object: The object affected by the action.
- Action: The type of operation performed:
- Create: Indicates that a user has created an object.
- Edit: Indicates that a user has edited an object.
- Delete: Indicates that a user has deleted an object.
Log Propagation
Logs are propagated across all affected entities. For example, when a note referencing an entity is created, an edit log for that entity is automatically generated. The example below illustrates this propagation, where the admin’s creation of a note referencing the entity PTI-... triggers an edit log on that entity.